
A Quick reference cheat sheet for data preparation using SQL in data science. From data profiling, validating, cleaning, deriving new attributes, standardizing to combining and splitting datasets.
- Introduction
- Understanding the Importance of Data Preparation
- SQL: A Versatile Tool for Data Preparation
- Data Preparation: Cheat Sheet
- Summary
- FAQs
- Q1. How do I handle missing or null values in SQL?
- Q2. How can I remove duplicate rows in SQL?
- Q3. What SQL techniques can I use for data validation?
- Q4. How do I handle inconsistent data formats in SQL?
- Q5. How can I merge or consolidate data from multiple tables in SQL?
- Q6. What SQL techniques are useful for handling outliers and anomalies?
- Learn more about other or related topics
Introduction
In the world of data analysis, data preparation is a crucial step that often gets overlooked. Before you can derive meaningful insights from your data, you need to ensure that it’s clean, consistent, and structured in a way that facilitates efficient analysis. This is where SQL (Structured Query Language) comes into play as a powerful tool for data preparation.
Understanding the Importance of Data Preparation
Data preparation is the process of transforming raw data into a format that is suitable for analysis. This can involve tasks such as cleaning, filtering, merging, and reshaping data. Neglecting this step can lead to inaccurate or misleading results, which can have serious consequences for businesses and organizations.
SQL: A Versatile Tool for Data Preparation
SQL is a domain-specific language designed for managing and manipulating relational databases. While it is primarily used for querying and modifying data, SQL also offers a wide range of functions and operations that make it an excellent choice for data preparation tasks.
Cleaning Data with SQL
One of the most common data preparation tasks is cleaning data. SQL provides a variety of functions and operations that can help you identify and handle missing values, remove duplicates, and standardize data formats. For example, you can use the CASE statement to handle missing values, the DISTINCT clause to remove duplicates, and string manipulation functions like TRIM and REPLACE to standardize text data.
-- Handling missing values
UPDATE table_name
SET column_name = COALESCE(column_name, replacement_value)
WHERE column_name IS NULL;
-- Removing duplicates
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name;
-- Standardizing text data
UPDATE table_name
SET column_name = TRIM(REPLACE(REPLACE(column_name, 'old_value', 'new_value'), 'old_value2', 'new_value2'));Filtering and Merging Data with SQL
SQL also provides powerful tools for filtering and merging data from multiple sources. You can use the WHERE clause to filter data based on specific conditions, and the JOIN operations to combine data from multiple tables based on related columns.
-- Filtering data
SELECT *
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
-- Joining tables
SELECT t1.column1, t1.column2, t2.column3, t2.column4
FROM table1 t1
JOIN table2 t2 ON t1.key_column = t2.key_column;Reshaping Data with SQL
In some cases, you may need to reshape your data to fit the requirements of your analysis. SQL offers functions and operations for pivoting, unpivoting, and aggregating data, allowing you to transform your data into the desired format.
-- Pivoting data
SELECT column1, column2, column3, column4
FROM (
SELECT column1, column2, column_name, column_value
FROM table_name
UNPIVOT (column_value FOR column_name IN (column3, column4)) AS unpivot_table
) AS pivot_table
PIVOT (
MAX(column_value) FOR column_name IN ('column3', 'column4')
) AS pivot_table;
-- Aggregating data
SELECT column1, column2, SUM(column3) AS total_column3
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column1, column2;Data Preparation: Cheat Sheet
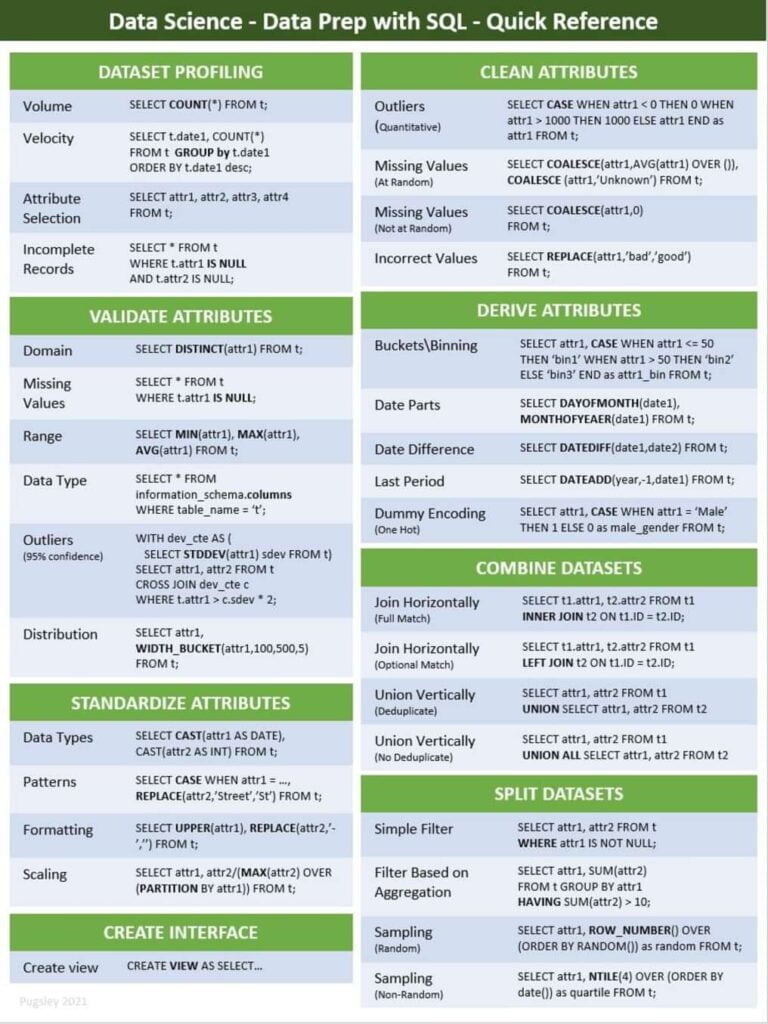
Summary
Data preparation is a critical step in the data analysis process, and SQL provides a powerful set of tools to tackle various data preparation tasks. By leveraging SQL’s capabilities for cleaning, filtering, merging, and reshaping data, you can ensure that your data is ready for accurate and meaningful analysis. Whether you’re working with structured or semi-structured data, SQL’s versatility makes it an indispensable tool in your data preparation toolkit.
FAQs
Q1. How do I handle missing or null values in SQL?
There are several ways to handle missing or null values, depending on your requirements. You can use the COALESCE function to replace nulls with a default value, IS NULL to filter out nulls, or ISNULL to check for nulls and take different actions accordingly.
Q2. How can I remove duplicate rows in SQL?
To remove duplicate rows, you can use the DISTINCT keyword along with your select statement. Alternatively, you can create a temporary table and insert only unique rows using SELECT DISTINCT or the ROW_NUMBER() function to identify and remove duplicates.
Q3. What SQL techniques can I use for data validation?
SQL provides various techniques for data validation, such as CHECK constraints to enforce data rules, UNIQUE constraints to prevent duplicate values, and FOREIGN KEY constraints to ensure referential integrity. You can also use SQL functions like REGEXP or LIKE to validate data formats and patterns.
Q4. How do I handle inconsistent data formats in SQL?
Inconsistent data formats can be a challenge for data cleaning. You can use SQL string functions like REPLACE, SUBSTRING, TRIM, and regular expressions to standardize data formats. Additionally, you can create user-defined functions or stored procedures to encapsulate complex formatting logic.
Q5. How can I merge or consolidate data from multiple tables in SQL?
To merge or consolidate data from multiple tables, you can use SQL JOIN operations like INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, or FULL OUTER JOIN. Depending on your requirements, you may also need to use aggregate functions like SUM, COUNT, or GROUP BY to combine data appropriately.
Q6. What SQL techniques are useful for handling outliers and anomalies?
To handle outliers and anomalies, you can use SQL functions like PERCENTILE_CONT or NTILE to identify and filter out extreme values. Alternatively, you can create temporary tables or views to isolate potential anomalies for further investigation or manual review.
Learn more about other or related topics
- SQL Most Common Tricky Questions
- Oracle Interview Questions
- How To Use SQL? An Ultimate Beginners Guide
- SQL Interview Questions for Beginner Level
- What is SQL? by AWS
