
Snowflake is a modern cloud-based data platform designed for data warehousing, data analysis, and data engineering. It’s the first cloud-built data platform, allowing data specialists to create both data warehouses and cloud data lake-houses.
It can manage both structured and unstructured data with ease. Its architecture is cloud-agnostic, meaning it works seamlessly across Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Lets explores its one of the unique feature called as “The Time Travel“.
Table of Content:
- Introduction
- Understanding the Concept of Time Travel
- Benefits of Snowflake Time Travel
- How Snowflake Time Travel Works
- Setting up Snowflake Time Travel
- Enabling Time Travel on Tables
- Querying Historical Data with Time Travel
- Restoring Data with Time Travel
- Limitations of Snowflake Time Travel
- Best Practices for Using Time Travel
- Monitoring and Managing Time Travel
- Use Cases of Snowflake Time Travel
- Comparing Snowflake Time Travel with Other Solutions
- Future Developments in Snowflake Time Travel
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- 1. Is Snowflake Time Travel a separate feature or included in the standard Snowflake subscription?
- 2. Can users query historical data across multiple tables using Snowflake Time Travel?
- 3. What is the impact of enabling Time Travel on storage costs for large datasets?
- 4. How does Snowflake ensure the security and compliance of historical data accessed through Time Travel?
- 5. What are some of the common use cases for Snowflake Time Travel in real-world scenarios?
- Learn more about other or related topics
Introduction
Snowflake Time Travel is a unique feature offered by Snowflake, a cloud-based data warehousing platform, that allows users to access and analyze data at different points in time. This revolutionary capability is changing the way organizations manage and utilize their data, offering a level of flexibility and control that was previously unimaginable.
Understanding the Concept of Time Travel
In the world of data management, Time Travel refers to the ability to query and retrieve data as it existed at a specific point in the past. This can be incredibly useful for debugging, auditing, compliance, and historical analysis purposes. Snowflake takes this concept to the next level by enabling users to access data not just from the past, but from any point within a specified time range.
Benefits of Snowflake Time Travel
One of the key benefits of Snowflake Time Travel is its simplicity and ease of use. Users can effortlessly query historical data without the need for complex configurations or additional infrastructure. This feature also enhances data governance, as it provides a complete audit trail of all changes made to the data over time.
How Snowflake Time Travel Works
Snowflake Time Travel works by automatically capturing and storing data at regular intervals, creating a virtual history of the database. This allows users to query past snapshots of the data without affecting the current state of the database. Time Travel is implemented at the table level, giving users granular control over which tables are enabled for historical querying.
Example with Code
Snowflake has a lot of features that can assist us to get out of the situation even though if we made a mistake. To restore the Employee Table to its previous condition before the erroneous update command, we will employ Query History and Time Travel. We also look some examples on DROP- UNDROP and how to CLONE an table.
Create a Sample Table
Lets create a sample table Employee with some data
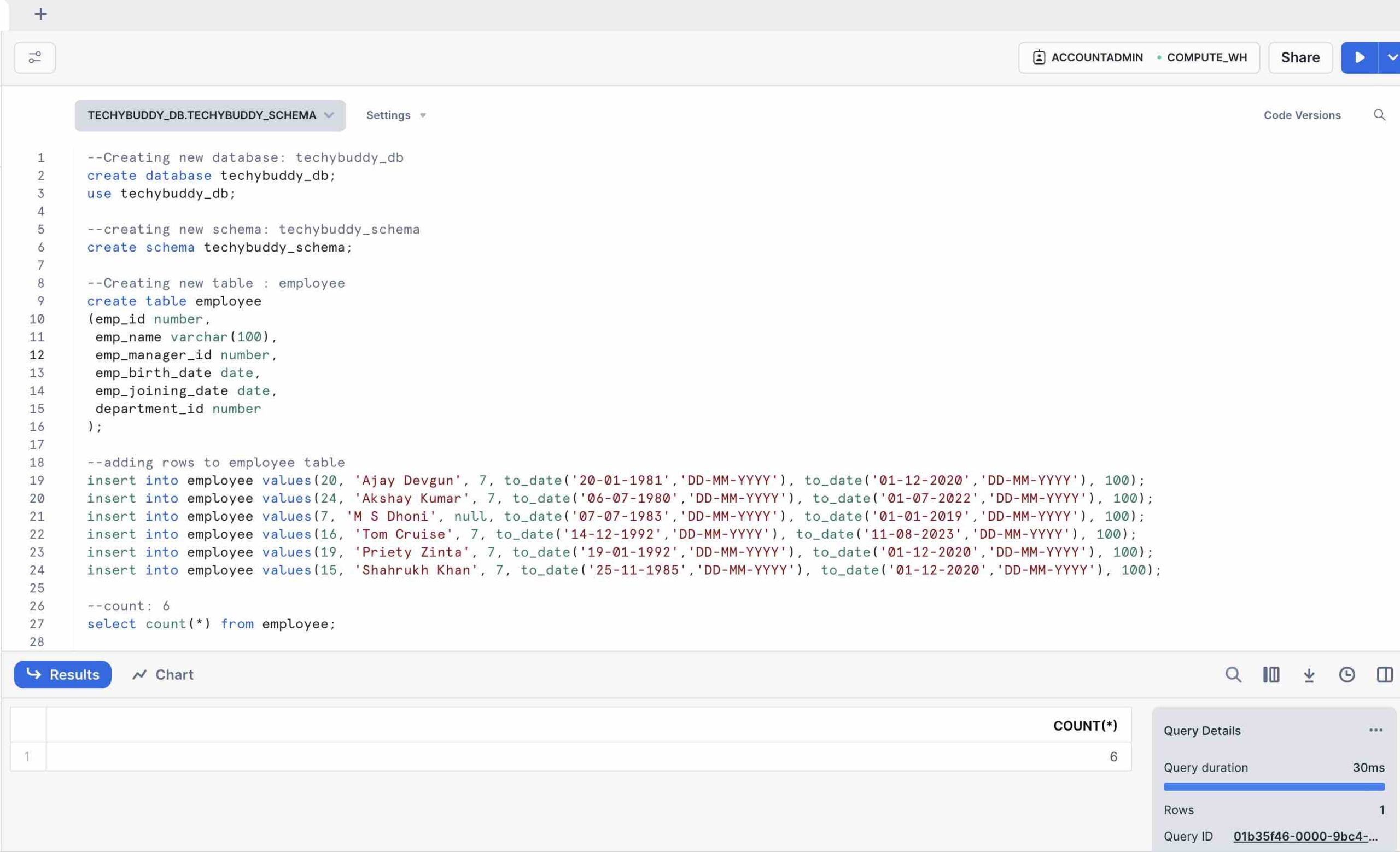
Showing data in Table : Employee
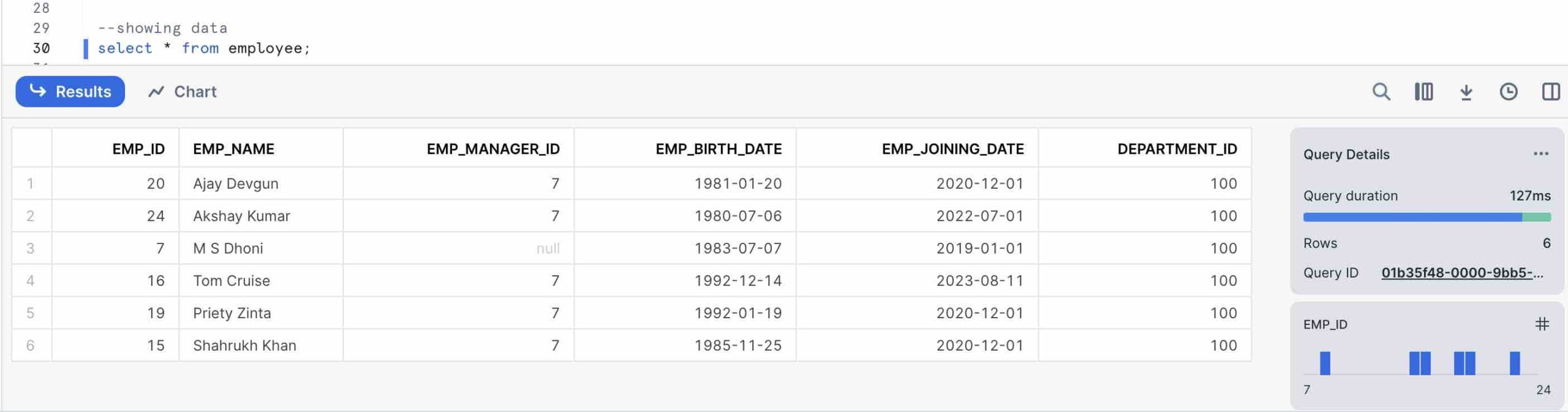
Update Table with Incorrect Value
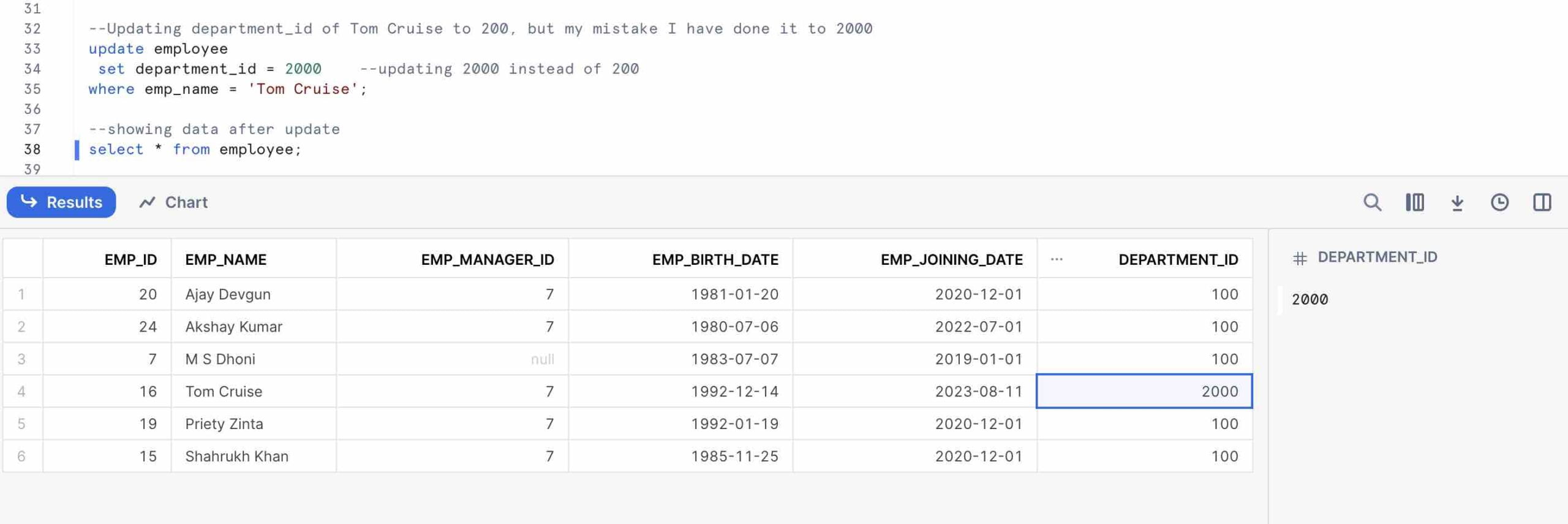
Updating department_id of an employee named Tom Cruise to 200, but my mistake I have done it to 2000.
Query History
Getting a list of all update statements we have made on Employye table. Same statement can be used for checking all historical queries that we ran on any a particular table.
--Query History: Getting a list of all update statements we have made
SELECT
query_id,
query_text,
user_name,
query_type,
start_time
FROM TABLE(techybuddy_db.information_schema.query_history())
WHERE 1=1
AND query_type = 'UPDATE'
AND query_text LIKE '%employee%'
ORDER BY start_time DESC;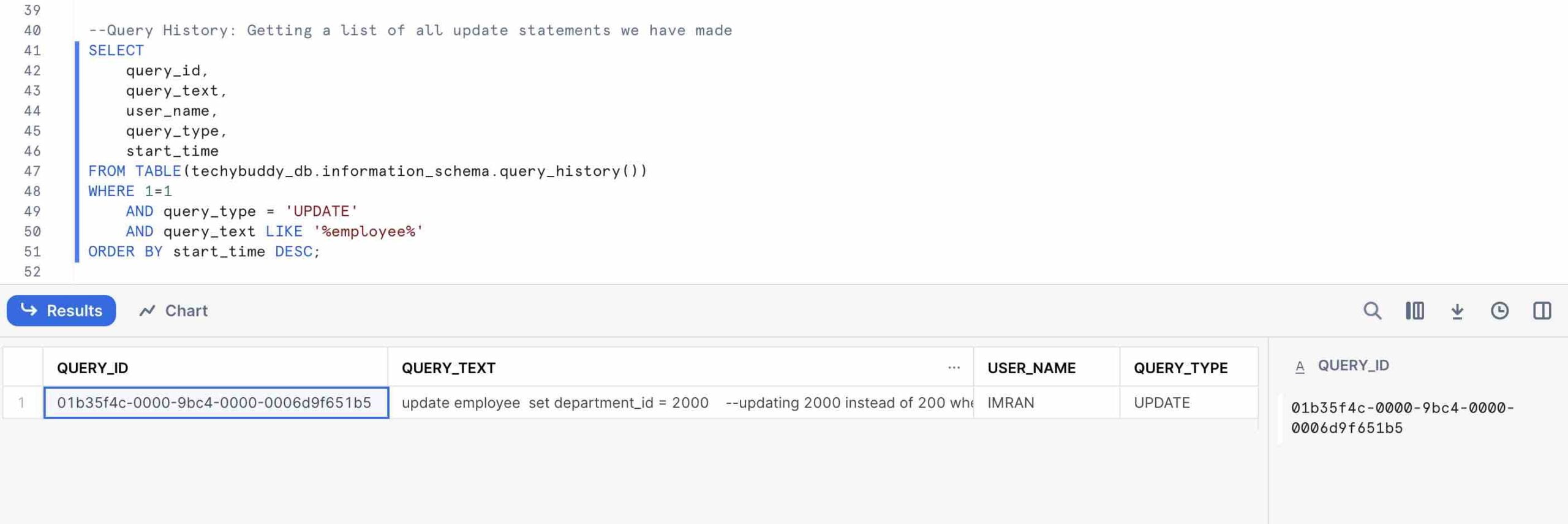
Getting Table Back Using Time Travel
--getting data at particular timestamp
SELECT * FROM my_table AT(TIMESTAMP => 'Mon, 01 Apr 2024 12:00:00 -0000'::timestamp_tz);
--getting data at particular time say 10 minutes before
SELECT * FROM my_table AT(OFFSET => -60*10);
--getting data before an statement using query-id
SELECT * FROM my_table BEFORE(STATEMENT => 'query_id');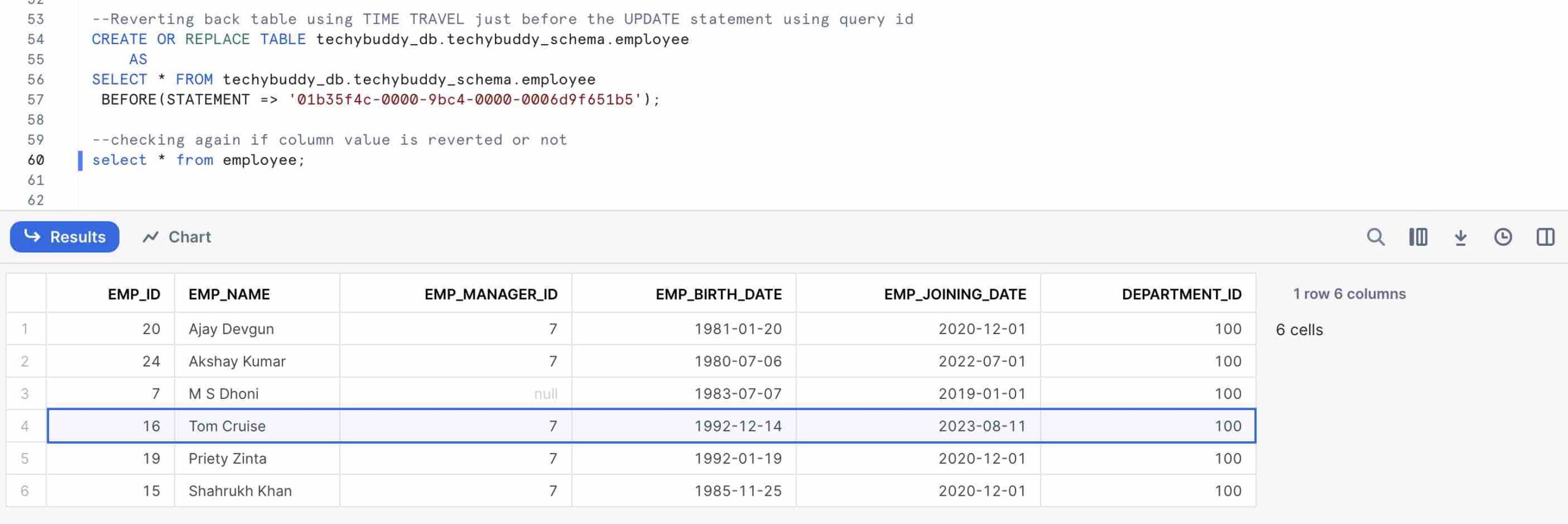
Other Time Travel statement options that we can utilise to get the data from history
- AT: The AT keyword indicates that any modifications made by a statement or transaction with a timestamp equal to the given parameter are included in the request.
- BEFORE: The BEFORE keyword indicates that the request is made with reference to the point that comes right before the given parameter.
- TIMESTAMP: Provides a precise time and date for Time Travel.
- OFFSET: Indicates the time difference in seconds to be used for time travel.
- STATEMENT: Indicates the statement’s query ID to use as the Time Traveler’s starting point.
Dropping and Un-dropping a Table
Dropping a table and then check if it has dropped or not
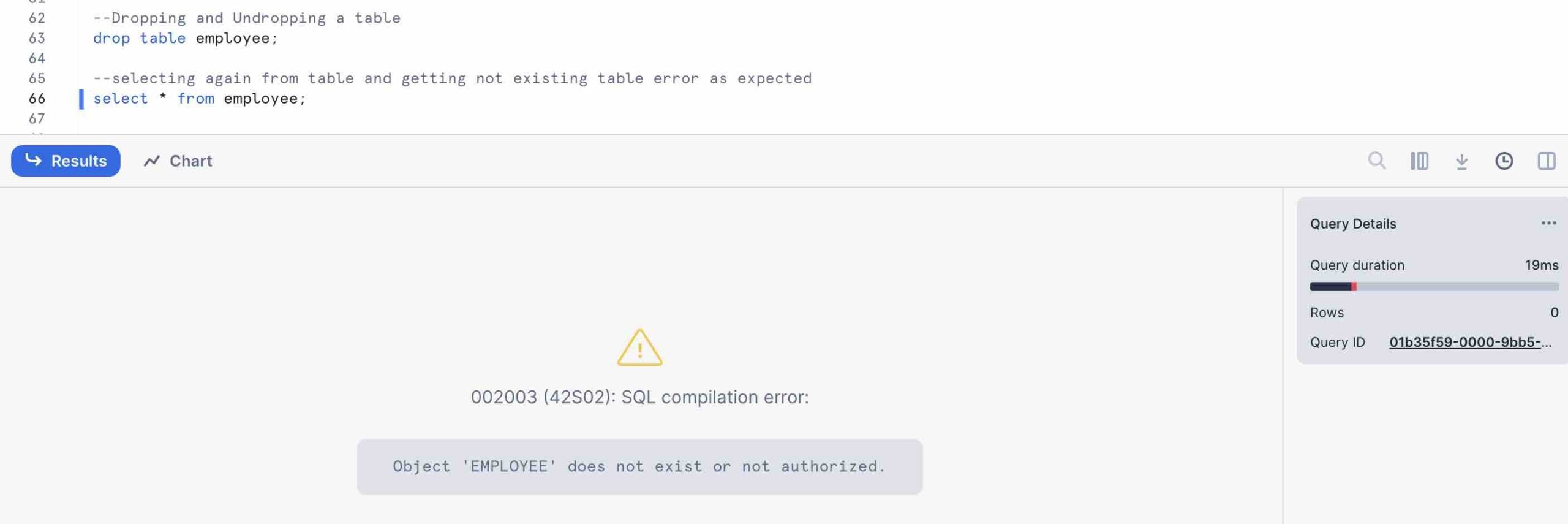
Un-dropping a table back to its original
--UNDROP to get the table back
UNDROP TABLE <table_name>;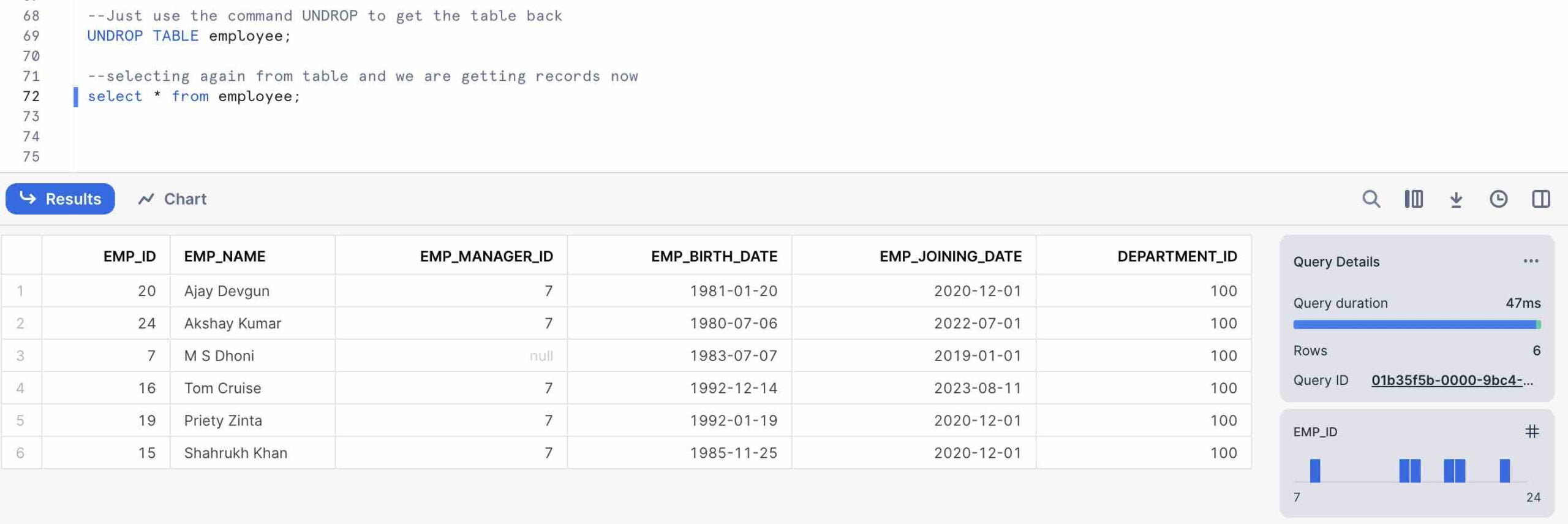
Clone an Existing Table
We can utilise this feature for cloning a Production table to Development environment to mimic production environment while developping. Here we are cloning an existing Employee table.
--General Syntax
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] TABLE [ IF NOT EXISTS ] <clone_table_name> CLONE <Your_source_table_name>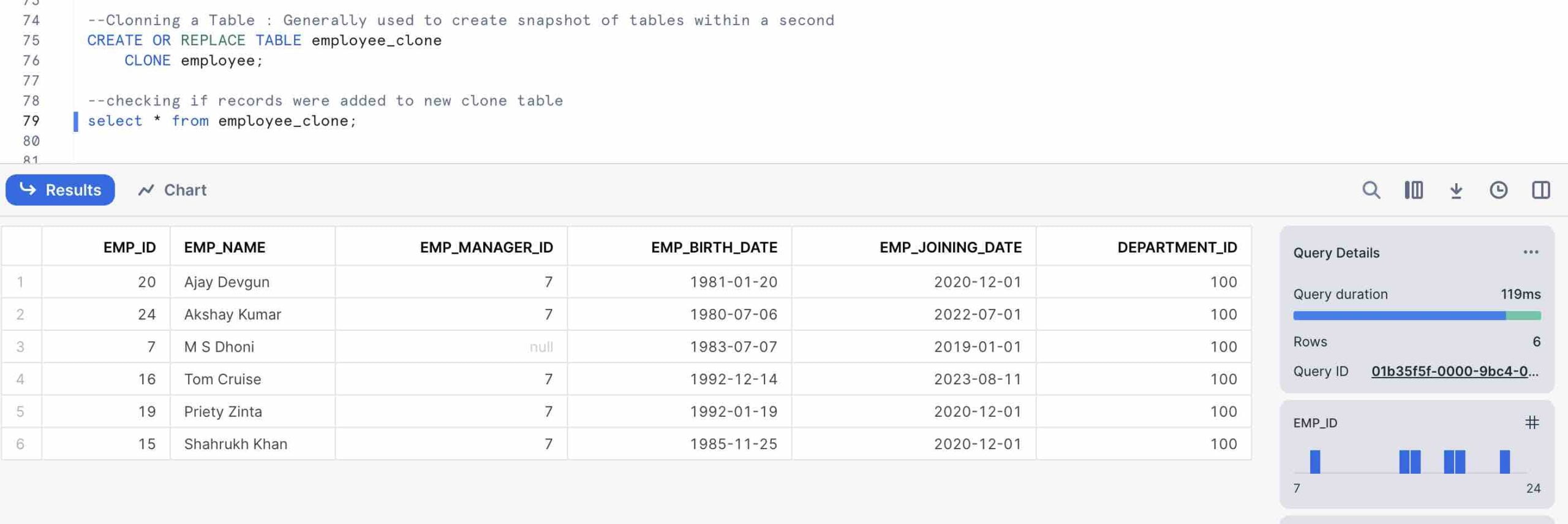
Zero Copy Cloning
You can make a duplicate of a database, schema, or table. When the clone is generated a snapshot of the data contained in the source object is obtained and made available to the cloned object. The cloned object is separate from the clone source and can be edit separately. In other words, modifications made to the clone object or the source object are independent of each other.
Syntax for Cloning Database and Schema
--General Syntax
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] { DATABASE | SCHEMA } [ IF NOT EXISTS ] <object_name> CLONE <source_object_name>
--Cloning using a Time Travel (if you want not to replace current database or schema)
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] { DATABASE | SCHEMA } [ IF NOT EXISTS ] <object_name> CLONE <source_object_name> AT (TIMESTAMP => <timestamp>)
--Ignore Tables while cloning
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] { DATABASE | SCHEMA } [ IF NOT EXISTS ] <object_name> CLONE <source_object_name> IGNORE TABLES WITH INSUFFICIENT DATA RETENTIONSetting up Snowflake Time Travel
To enable Time Travel on a Snowflake table, users simply need to specify a time travel retention period during the table creation process. This retention period determines how far back in time users can query the data. By default, Snowflake retains data for 24 hours, but this can be extended to up to 90 days for an additional cost.
Enabling Time Travel on Tables
Users can enable Time Travel on specific tables by using the AS OF TIMESTAMP or AS OF SYSTEM TIME query clauses. These clauses allow users to access the data at a specific point in time, either based on a timestamp or a system time. This gives users the flexibility to retrieve historical data with precision and accuracy.
Querying Historical Data with Time Travel
Once Time Travel is enabled on a table, users can query historical data using standard SQL syntax. Snowflake automatically handles the retrieval of the correct data snapshot based on the specified timestamp or system time. This feature simplifies the process of analyzing past data and conducting trend analysis without the need for complex data manipulation.
Restoring Data with Time Travel
In addition to querying historical data, Snowflake Time Travel also allows users to restore data to a previous state. By leveraging the RESTORE command, users can roll back changes made to a table and revert to a specific point in time. This feature provides an added layer of data protection and recovery capabilities, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
Limitations of Snowflake Time Travel
While Snowflake Time Travel offers immense benefits, it also has certain limitations. The cost of storing historical data beyond the default retention period can add up, especially for large datasets. Additionally, enabling Time Travel on tables with high write activity can impact performance and storage usage. It is essential for users to carefully plan and manage Time Travel to optimize its usage and minimize additional costs.
Best Practices for Using Time Travel
To maximize the benefits of Snowflake Time Travel, users should follow best practices such as setting appropriate retention periods, managing storage costs, and monitoring query performance. It is also recommended to regularly review and audit historical data to ensure compliance with data governance policies and regulations. By following these best practices, users can effectively leverage Time Travel for their data management needs.
Monitoring and Managing Time Travel
Snowflake provides comprehensive monitoring and management tools for Time Travel. Users can track historical data usage, analyze query performance, and optimize storage costs through the Snowflake interface. Additionally, Snowflake offers built-in features for data protection and security, ensuring that historical data remains secure and compliant with industry standards.
Use Cases of Snowflake Time Travel
Snowflake Time Travel is ideal for a wide range of use cases, including financial analysis, regulatory compliance, and historical trend analysis. Organizations in highly regulated industries such as healthcare, finance, and government can benefit from Time Travel’s data governance and audit capabilities. Moreover, businesses with complex data management requirements can use Time Travel to simplify and streamline their data analysis processes.
Comparing Snowflake Time Travel with Other Solutions
When compared to traditional data management solutions, Snowflake Time Travel stands out for its simplicity, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Unlike on-premises data warehouses, Snowflake eliminates the need for manual backups and restores, reducing operational overhead and improving data reliability. Moreover, Snowflake’s cloud-native architecture enables seamless integration with other cloud services, providing a unified data ecosystem for organizations of all sizes.
Future Developments in Snowflake Time Travel
As Snowflake continues to innovate and expand its capabilities, we can expect to see further enhancements to Time Travel functionality. Future developments may include advanced analytics features, real-time data processing capabilities, and deeper integration with external data sources. Snowflake’s commitment to delivering cutting-edge data management solutions ensures that Time Travel will remain a key feature for organizations seeking to unlock the full potential of their data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Snowflake Time Travel is a game-changing feature that revolutionizes the way organizations manage and analyze their data. By providing users with the ability to query historical data at any point in time, Snowflake empowers organizations to make informed decisions, ensure data integrity, and drive business innovation. With its simplicity, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, Snowflake Time Travel is reshaping the future of data management and unleashing new possibilities for organizations across industries.
FAQs
1. Is Snowflake Time Travel a separate feature or included in the standard Snowflake subscription?
Snowflake Time Travel is included in all Snowflake subscriptions, with the ability to customize retention periods based on the user’s needs.
2. Can users query historical data across multiple tables using Snowflake Time Travel?
Yes, users can query historical data across multiple tables by specifying the relevant timestamps or system times in their queries.
3. What is the impact of enabling Time Travel on storage costs for large datasets?
Enabling Time Travel on large datasets can increase storage costs, especially when extending the retention period beyond the default settings. Users should carefully monitor and manage storage usage to optimize costs.
4. How does Snowflake ensure the security and compliance of historical data accessed through Time Travel?
Snowflake employs robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and audit logging to protect historical data accessed through Time Travel. Compliance features such as data masking and anonymization further enhance data security and privacy.
5. What are some of the common use cases for Snowflake Time Travel in real-world scenarios?
Real-world use cases for Snowflake Time Travel include analyzing financial data for auditing purposes, tracking customer behavior over time for marketing analysis, and conducting risk assessments based on historical trends. Organizations across industries can leverage Time Travel to gain valuable insights and drive strategic decision-making based on historical data.
Learn more about other or related topics
- AWS Redshift Vs Snowflake: How To Choose?
- NoSQL Vs SQL Databases: An Ultimate Guide To Choose
- Tableau: A Quick Refresher and Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- What’s new in Oracle 19c and how does its architecture work?
